How does the respiratory system work ? The secrets
Caution : You must consult your doctor for your health. This page presents only a personal and alternative point of view which should not be considered as an attempt to prescribe medicine.
As long as you are in good health, it is rare that you are interested in your breathing.
So we breathe all the time without even realizing it.
It seems simple and normal.
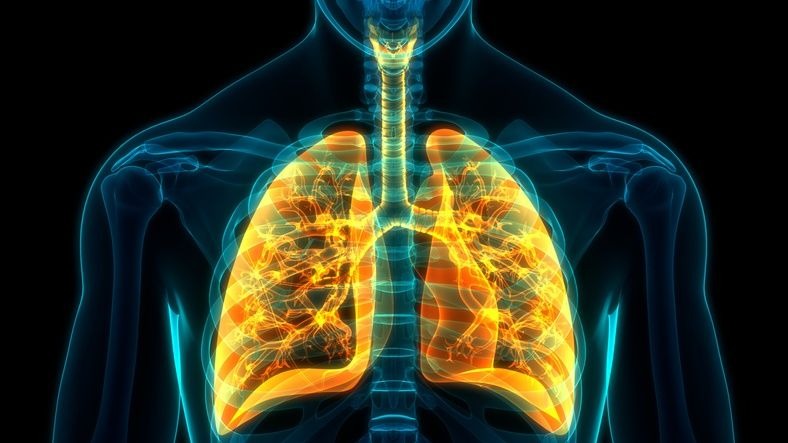
But in reality, it is a rather complex phenomenon which involves several organs of the body.
These various organs form a whole called: respiratory system.
It would be nice to take a moment to learn a bit about everything that contributes to our breathing.
What is the respiratory system and how does it work? The answer here.
What is the breathing system?
We breathe naturally through the nose and sometimes through the mouth (under stress).
But what you don't know is that the process is much more complex than that.
There are actually several other organs that come into play.
It includes all the organs allowing:
- breathe in the air necessary to provide oxygen to the body;
- and to exhale the carbon dioxide to evacuate the excess carbon dioxide;
The respiratory system is therefore made up of many organs acting in perfect symbiosis.
In addition to the nose and mouth, there are in particular:
- the larynx,
- the pharynx,
- the trachea,
- bronchitis,
- the alveoli,
- the bronchioles,
- the lungs,
- and the diaphragm.
These are the different organs that make up the respiratory system.
How does the respiratory system work?
Breathing is a natural phenomenon.
Basically, it consists of inhaling and exhaling the air in the body.
However, the contribution of the various bodies involved is necessary for this process to succeed.
Already, you should know that everything is based on the mechanism of respiration or pulmonary ventilation.
It is the inspiration and the expiration.
Then there are gas exchanges and transport.
Here is the whole process.
Pulmonary ventilation
As stated earlier, pulmonary ventilation takes place in two phases, namely inspiration and expiration.
The diaphragm muscle plays a very important role during inspiration.
Indeed, to inflate the lungs, it contracts, accompanying the intercostal muscles with it, especially during physical exertion.
The diaphragm moves on its own when you are at rest.
Regarding the expiration, it does not involve any muscular effort.
After air has entered the body, the diaphragm returns to its starting position.
The lungs therefore deflate and thereby expel carbon dioxide to the outside.
This is how pulmonary ventilation works.
Respiratory exchanges
The respiratory system is not limited to pulmonary ventilation.
The body needs oxygen to function well.
This is where the respiratory exchanges come into play.
Here too there are two phases.
Internal respiration and external respiration.
The first concerns the exchange of gases between systemic capillaries (including the cardiovascular system) and muscle cells.
It is this process that allows oxygen to be distributed to the different tissues (cells).
External respiration, for its part, concerns the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
To do this, it uses the alveolar-capillary membrane.
External respiration allows an association between hemoglobin and oxygen inside the pulmonary capillaries.
In other words, the oxygen inhaled by attaching itself to the red blood cells (hemoglobin) of your blood.
As for carbon dioxide, it enters the alveoli after separating from the blood.
Thus the respiratory exchanges take place.
The transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Oxygen, which plays a very important role for our body, enters the lungs through respiration.
The red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen to the whole body.
During transport, it takes on a complex shape with hemoglobin.
This is called oxyhemoglobin.
Carbon dioxide, on the other hand, is carried in the blood as a dissolved gas.
It also takes on a complex shape when transported with hemoglobin.
Blood is therefore the main channel used for the transport of gas exchanges.
Breathing is a fairly complex phenomenon that interacts closely with the cardiovascular and muscular systems.
During exercise, muscles consume a lot of oxygen and produce carbon dioxide.
Therefore, once physical activity increases, the respiratory rate will increase simultaneously with the heart rate.
It will thus provide the muscles with oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide.
The secret of oxygenation
There is a widespread belief that humans should do anything to expel all CO2 because carbon dioxide is toxic.
This is completely wrong!
Excess CO2 is toxic, but a minimum concentration is required in the body.
CO2 maintains the acid-base balance of the blood but also that of the cells (we speak of Ph).
CO2 has 3 basic physiological effects (oxygenation, sedation and dilation).
1) by producing CO2 through physical activity, you attract more oxygen to yourself (this is the whole point of being active and eliminating a sedentary lifestyle).
This attraction phenomenon between CO2 and oxygen is called the Bohr effect.
Your blood will release oxygen only in cells that produce CO2.
2) CO2 is also a molecule having a sedative, soothing and calming effect.
It is probably the best anti-depressant there is.
3) CO2 also has an expansion effect.
This is why you should NEVER breathe out all the air in your lungs.
Indeed, there is a dead space in your lungs, it contains a good dose of CO2 necessary to maintain the dilation of your pulmonary alveoli.
Above all, don't listen to therapists asking you to breathe out all the air in your lungs as much as possible, it's unnatural.
In conclusion
The respiratory system is a complex whole.
But the most important thing will be to listen to your body, to breathe quietly and calmly, in order to optimize your cellular oxygenation.
❤ The ultimate guide to breathing
Intermittent Breathing : Discover the method to quickly relieve your anxiety and chronic fatigue (positive effects from the first use).Read also :
Previous article : How to work and train the lungs?
Next article : How does breathing affect the heart rate?

